Clustering¶
Normalization¶
When integrating multiple samples, the normalization is executing during the integration.
Note
Currently, the recommendation of Seurat’s team is to use the standard “RNA” assay when performing differential expression (D.E) analysis and for data visualization, even when using SCTransform (See here). Therefore, Asc-Seurat will use the SCTransformed data (“SCT” assay) until the clustering step only.
To use the “RNA” assay after SCTransform, Asc-Seurat will automatically perform the LogNormalization and scaling of the data in the RNA assay by applying the default parameters.
Dimensional reduction (PCA)¶
The PCA will be executed using Seurat’s function RunPCA and, after its conclusion, an elbow plot is generated automatically, to help users to decide how many PCs should be included to inform the clustering step.
Users can use this plot to select the PCs with the highest standard deviation (more informative PCs). Also, users should set the number of PCs to include during clustering in the windows at the plot’s right side.
In the example below, the first 20 PCs are selected. Not that the resulting plot will be slightly different depending on the normalization method. Below we show the result obtained using LogNormalization.
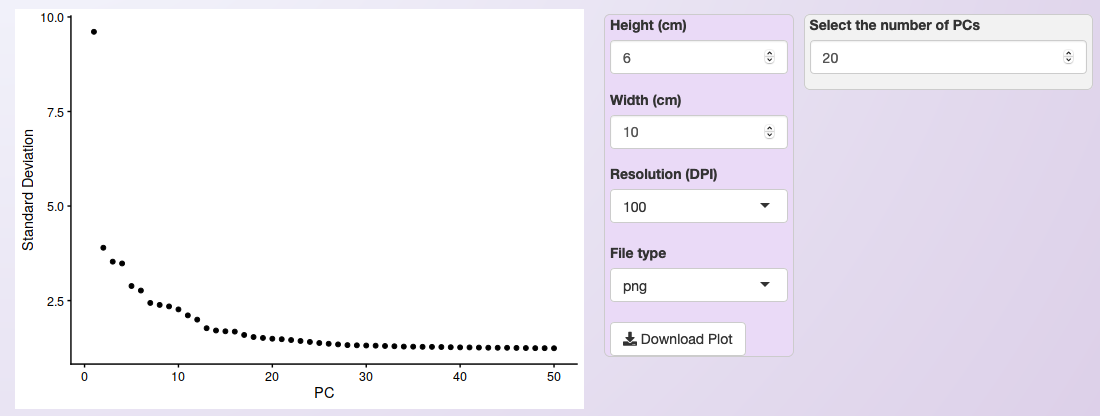
Elbow plot provided to help to select the most informative PCs. For the PBMC integrated dataset, and using the LogNormalization method, we chose the 20 first PCs.¶
Clustering of cells¶
The next step is the clustering of the cells. For that, Asc-Seurat used both FindNeighbors and FindClusters functions of the Seurat package.
Before the execution, however, users need to set a value for the resolution parameter. The resolution is an important parameter to evaluate because it determines the profile and number of clusters identified for a dataset. Selecting larger values will favor splitting cells into more clusters while choosing a smaller value has the opposite effect. Quoting from Seurat’s tutorial: “We find that setting this parameter between 0.6-1.2 typically returns good results for single-cell datasets of around 3K cells. Optimal resolution often increases for larger datasets”.
Tip
There is no easy way to define an optimal value for the resolution parameter. Users need to try different values and evaluate the resulting clusters according to the expectation for their cells population. Visualizing the expression profile of cell-type-specific markers can provide a hint if the chosen value is too small or too large.
After the clustering step’s execution, three plots are generated for cluster visualization, all of them using the Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) technique. The first plot shows the clustering of the whole dataset colored by cluster. The second plot shows the same plot, but cells are colored by sample. The third plot shows the clustering of the cells of each sample, with one subplot per sample.
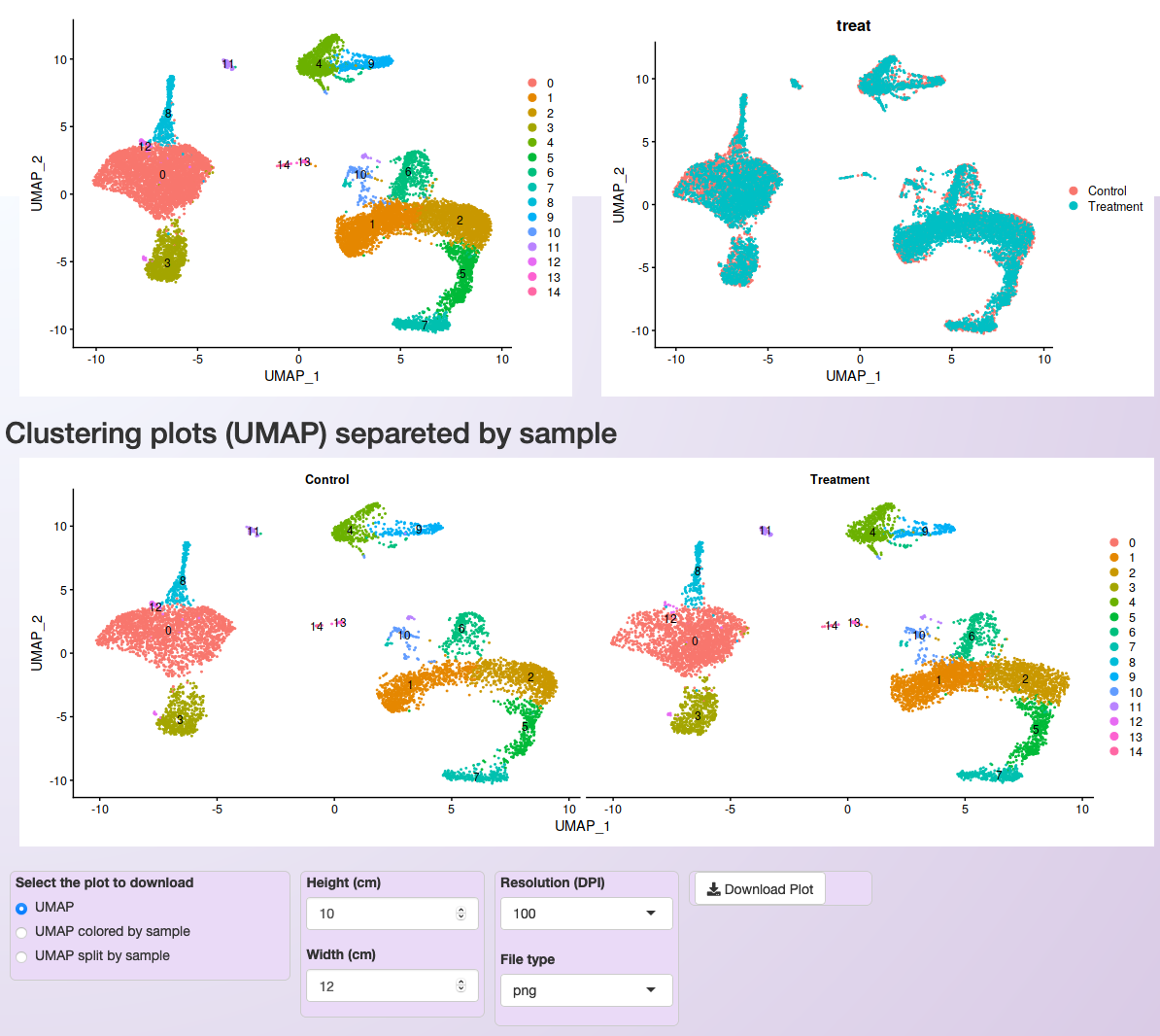
Plot showing the PBMC integrated dataset clustering using 20 PCs, LogNormalization, and a resolution value of 0.5.¶
Selecting clusters of interest¶
In some cases, it is interesting to select or exclude some clusters of cells from the dataset before executing the subsequent steps. This process is helpful, for example, when users desire to explore a developmental trajectory of a specific group of cell types.
Asc-Seurat makes this step simple. Users only need to select the cluster(s) to keep or exclude and start reanalysis of the remaining cells by clicking on Reanalyze after selection/exclusion of clusters (see below).

Asc-Seurat makes it easy to select or exclude a cluster (or clusters) of cells. In this example, we exclude all cells belonging to cluster 0.¶
Asc-Seurat will then execute the steps with the new set of cells up to the PCA. Then, users need to evaluate the elbow plot and decide the number of PCs to cluster the new set of cells. Users can either keep the same value for the resolution parameter or modify it before clicking on Run the clustering analysis to start the clustering once more.
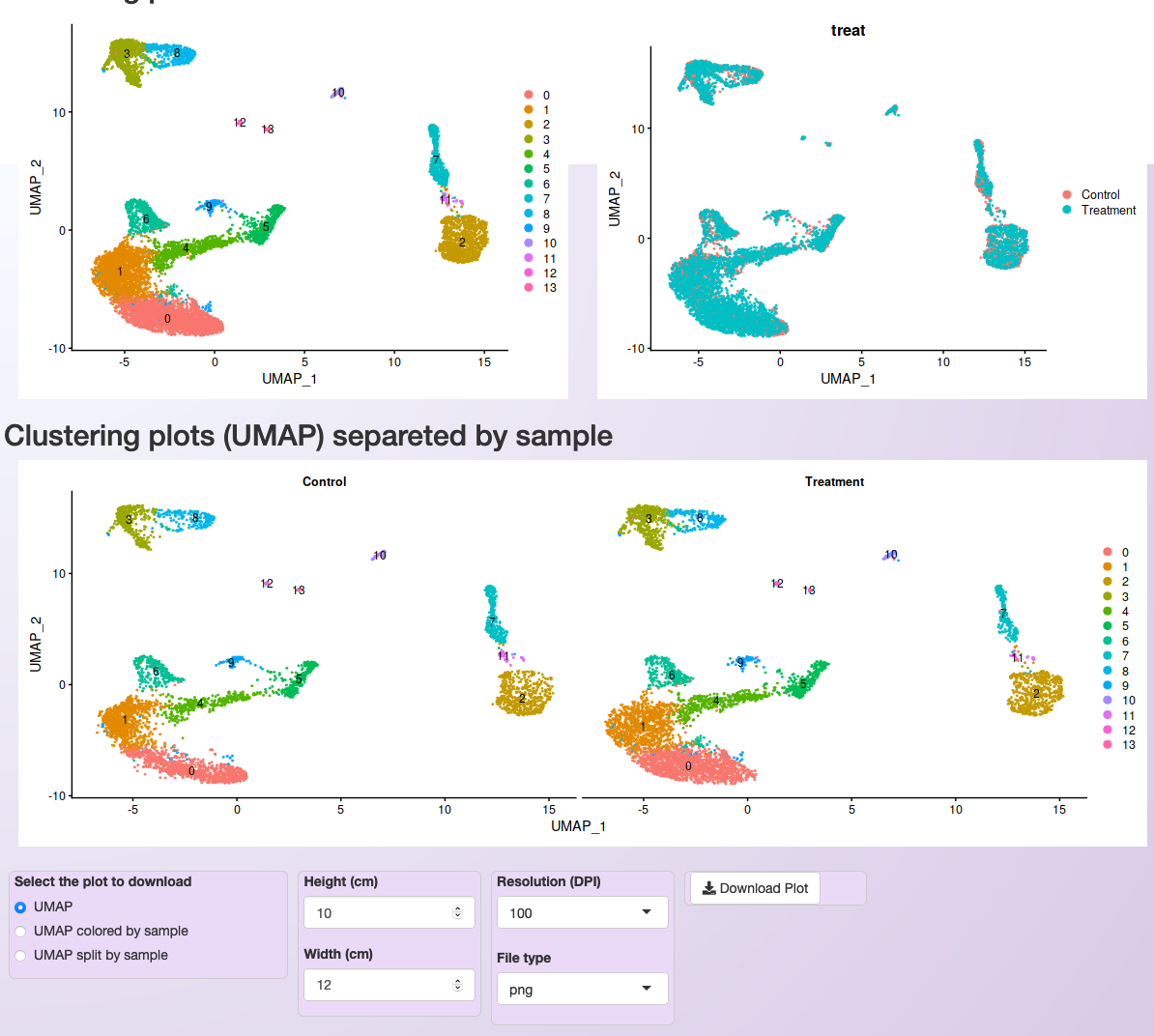
Clustering of the PBMC integrated dataset after excluding cells belonging to cluster 0 from the original dataset.¶
Warning
The cluster’s numbering will change every time that clusters are selected or excluded.